How 3D printing is shaping the manufacturing industry

Anúncios
3D printing is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by offering benefits such as cost efficiency, customization, rapid prototyping, and a reduced environmental impact through minimized waste.
How 3D printing is shaping the manufacturing industry is a question many are asking as we enter a new era of production. This innovative technology promises to redefine how we create products, offering efficiency and customization like never before. Are you ready to discover its potential?
Anúncios
Understanding 3D printing technology
Understanding 3D printing technology is essential as this innovation reshapes how products are made. It enables the creation of items layer by layer, offering immense flexibility and customization.
Basics of 3D Printing
At its core, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, allows for the production of complex shapes that traditional methods find challenging. This technology uses materials like plastics, metals, and even biological substances to manufacture objects.
Key Technologies in 3D Printing
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): A popular method that melts plastic filament to create layers.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Utilizes a laser to cure liquid resin into solid form.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Fuses powdered materials using a laser, allowing for stronger and more durable parts.
These processes open new possibilities in design and manufacturing. For instance, geometric complexity can be easily achieved with 3D printing, proving advantageous for prototyping.
Anúncios
Benefits of 3D Printing
The benefits of adopting 3D printing technology extend beyond manufacturing speed. Companies can reduce waste since materials are only used where needed. Production can be localized, which cuts costs and decreases environmental impact.
Moreover, this technology fosters innovation. Teams can rapidly iterate designs, making testing and refining easier than ever before. This speeds up time-to-market and enhances overall product quality.
Challenges in 3D Printing
However, it’s important to address challenges. The quality of materials and speed of production can vary. Additionally, there are concerns regarding intellectual property, as 3D models can be easily replicated.
As we embrace this technology, understanding the fundamentals allows companies to utilize 3D printing effectively. With the potential to revolutionize production, it’s a landscape worth exploring further.
Advantages of 3D printing in manufacturing
The advantages of 3D printing in manufacturing are numerous, and they change how companies think about production. This technology can significantly reduce costs and improve efficiency across various industries.
Cost Savings
One major benefit is cost savings. Traditional manufacturing often requires expensive tools and molds. With 3D printing, companies can produce parts directly from digital files, eliminating these costs. This method also reduces waste, as materials are only used where needed.
Customization
3D printing allows for a level of customization that is hard to achieve with traditional methods. Businesses can easily create unique products tailored to individual customer preferences without incurring hefty expenses.
Speed and Efficiency
Another advantage is the speed of production. 3D printing can drastically decrease lead times. Prototypes can be printed within hours, allowing for faster testing and refinement. This accelerates the entire design process and helps products reach the market more quickly.
Reduced Supply Chain Complexity
Additionally, it reduces supply chain complexity. Companies can produce parts locally, cutting down on transportation costs and delays. This flexibility can be a game-changer for businesses looking to adapt to market changes.
These factors combine to make 3D printing a powerful tool for modern manufacturers. As businesses look for innovative ways to stay competitive, embracing this technology offers a clear pathway to success.
Real-world applications of 3D printing
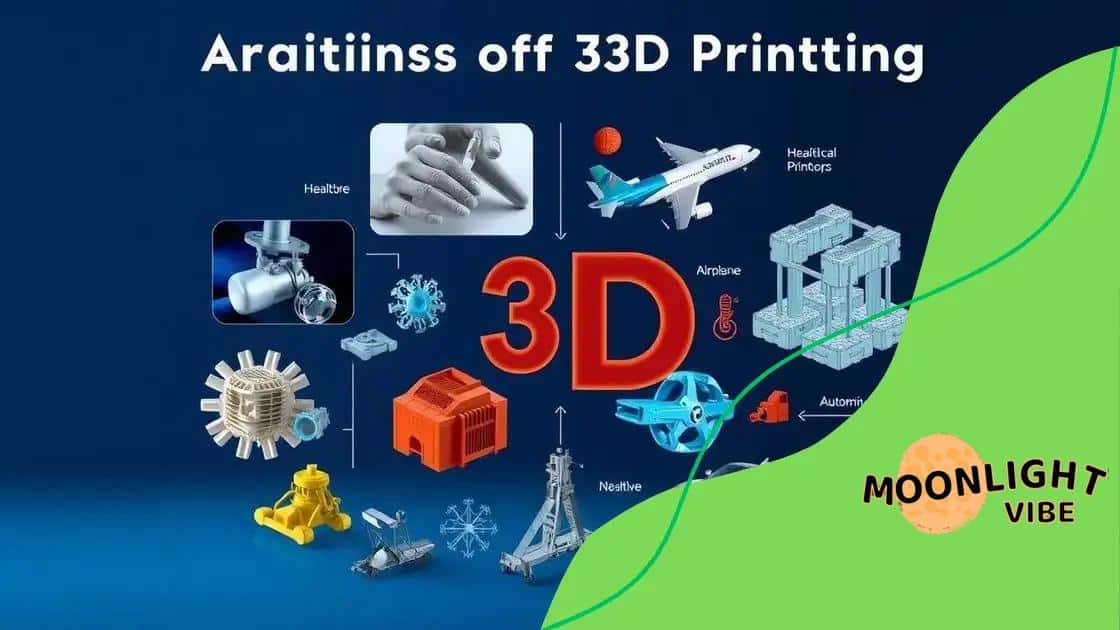
Real-world applications of 3D printing can be found across various industries, demonstrating its versatility and potential. This technology is making significant impacts in fields such as healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods.
Healthcare Innovations
In healthcare, 3D printing is revolutionizing the way medical devices and prosthetics are produced. Custom implants can be made to fit individual patients. Surgeons can create models of organs for practice before actual procedures, enhancing precision and outcomes.
Aerospace Advancements
In the aerospace sector, companies utilize 3D printing for lightweight parts, which improves fuel efficiency and reduces costs. Components that were once complex and expensive to manufacture can now be produced with ease and speed.
Automotive Uses
Similarly, the automotive industry has embraced this technology for prototyping and production. Car manufacturers can rapidly create parts for testing. This accelerates innovation and reduces the time needed to bring a new vehicle to market.
Consumer Goods
For consumer goods, 3D printing allows for personalized products, such as custom shoes and tailored eyewear. Businesses can respond quickly to consumer demands, producing products that fit individual styles without large inventories.
These examples show how 3D printing is not just a manufacturing tool but a catalyst for innovation. By integrating this technology, industries are changing their production concepts, improving efficiency, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Challenges faced in 3D printing adoption
The adoption of 3D printing technology is not without its challenges. Companies often face various obstacles that can hinder the successful implementation of this innovative production method.
Material Limitations
One of the primary challenges is the limitations of available materials. While many materials can be used in 3D printing, the range is still not as extensive as traditional manufacturing processes. Some materials may not provide the required strength or durability for certain applications.
Cost of Technology
The initial investment in 3D printing equipment can also be significant. High-quality printers and necessary software can be expensive, and not all businesses may be ready to make such an investment.
Skill Gaps
There are also skill gaps in the workforce. Many employees may lack the knowledge or training needed to operate 3D printing technology effectively. This can result in inefficiencies and errors, which can decrease productivity.
Quality Control Issues
Furthermore, ensuring quality can be a challenge. The technology is still evolving, and maintaining consistency in production can prove difficult. Companies may struggle to meet stringent quality standards set by clients or regulatory bodies.
Despite these challenges, many companies are exploring solutions and investing in 3D printing technology. As advancements continue, it is essential to address these barriers to fully realize its potential in manufacturing.
Future trends in 3D printing technology
Future trends in 3D printing technology promise to reshape various industries even further. As advancements continue, we can expect greater efficiency and new applications that enhance manufacturing practices.
Increased Material Diversity
One notable trend is the development of new printing materials. Researchers are discovering ways to use metals, ceramics, and biomaterials. This expanded range will allow for stronger and more versatile products.
Automation and AI Integration
Automation and artificial intelligence integration into 3D printing processes will also significantly impact production. Smart systems may soon optimize printing settings on-the-fly, reducing errors and improving quality.
Mass Customization
Another trend is mass customization. Businesses will increasingly offer personalized products designed to meet individual customer needs. This flexibility will attract consumers looking for unique solutions.
Sustainability Efforts
Sustainability will remain a key focus. The industry is looking at ways to reduce waste and energy consumption. Innovations like recycling old 3D prints into new materials will become more common, promoting a circular economy.
The growing applications of 3D printing technology indicate a bright future for the industry. From healthcare to aerospace, the possibilities are extensive, and companies that adapt to these changes will likely lead the market.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about 3D Printing Technology
What are the main benefits of 3D printing in manufacturing?
The main benefits include cost savings, customization, faster production times, and reduced waste.
What industries are currently using 3D printing technology?
Industries such as healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods are actively using 3D printing technology.
What challenges do companies face when adopting 3D printing?
Some challenges include material limitations, high initial costs, skill gaps in the workforce, and quality control issues.
What trends can we expect to see in the future of 3D printing?
Future trends include increased material diversity, automation, mass customization, and a focus on sustainability.





